Food Chains And Food Webs Answer Key: these terms often pop up in biology classrooms and research papers, representing fundamental concepts in ecology. They illustrate the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment, dictating the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. This article will delve into the intricacies of these ecological concepts, providing a comprehensive understanding of their structure, importance, and real-world applications.
Are you curious about how energy transfers from a tiny plant to a fearsome predator? Or how changes in one species population can ripple through the entire ecosystem? If so, you’ve come to the right place. We’ll explore the building blocks of food chains and food webs, the different trophic levels, and the factors that influence their stability and complexity.
Decoding the Food Chain
A food chain depicts a linear sequence of organisms, where each organism serves as a food source for the next. It starts with producers, like plants, that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Then, it moves up to consumers, the organisms that eat the producers. This process continues with secondary, tertiary, and even quaternary consumers.
For example, a simple food chain could be grass -> grasshopper -> mouse -> snake -> hawk. Each arrow represents the flow of energy from one organism to the next. The grasshopper consumes the grass, the mouse consumes the grasshopper, and so on.
Here at Mina Cones, we understand the importance of healthy eating habits, and learning about where our food comes from is an important part of that. Check out our curtis foods weekly ad for some great deals on fresh produce.
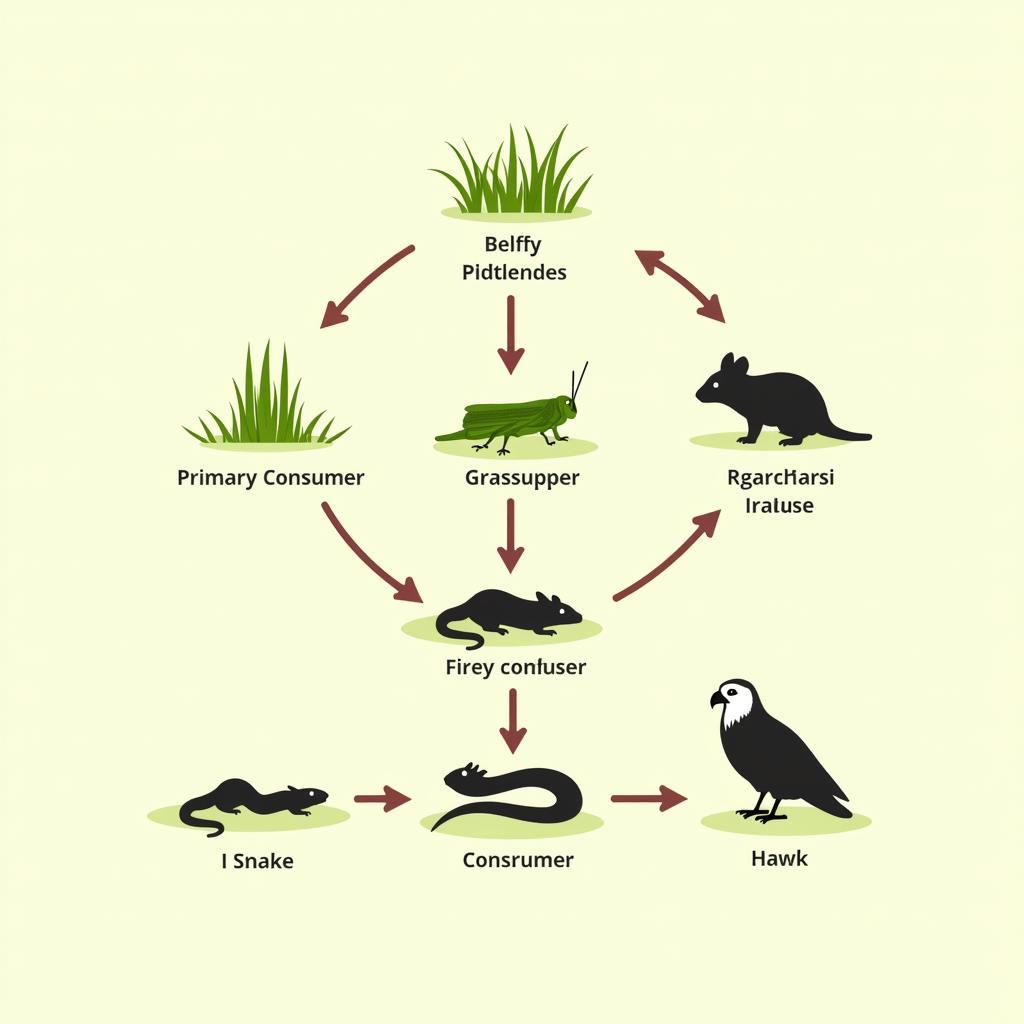 Food Chain in a Grassland Ecosystem
Food Chain in a Grassland Ecosystem
Exploring the Food Web: A Network of Life
A food web is a more complex and realistic representation of feeding relationships within an ecosystem. It’s a network of interconnected food chains, showcasing how multiple organisms can be part of different food chains simultaneously. This interconnectedness makes ecosystems more resilient to changes.
For instance, a hawk might not only eat snakes but also rabbits or squirrels. Similarly, a mouse might be preyed upon by a fox, an owl, or a snake. These multiple feeding relationships are what create a web-like structure.
Why are Food Webs Important?
Food webs are essential for ecosystem stability. They highlight the interdependence of species and how changes in one population can affect others. Understanding food webs helps us manage and conserve our natural resources effectively.
Looking for some fun activities related to food? Take a look at our fast food crossword puzzle.
 Complex Food Web in a Forest Ecosystem
Complex Food Web in a Forest Ecosystem
Trophic Levels: The Hierarchy of Energy Transfer
Within food chains and food webs, organisms are categorized into different trophic levels based on their feeding position. Producers occupy the first trophic level, followed by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers.
- Producers: Plants, algae, and some bacteria that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores that feed directly on producers.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores that eat primary consumers.
- Tertiary Consumers: Carnivores that eat secondary consumers.
- Decomposers: Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organisms and waste products, returning nutrients to the ecosystem.
“Understanding trophic levels is crucial for understanding how energy flows through an ecosystem,” explains Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned ecologist at the University of California, Berkeley. “Each trophic level plays a specific role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.”
Need some help understanding food chains and food webs better? Our food chains/webs worksheet answers can provide valuable support.
Food Chains and Food Webs: Answer Key to Ecosystem Dynamics
Food chains and food webs answer key questions about how ecosystems function. They demonstrate how energy is transferred, how populations interact, and how environmental changes can impact the entire system. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the delicate balance of nature and the importance of conservation efforts.
“Human activities can significantly impact food webs,” says Dr. David Miller, a wildlife biologist at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. “Habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change can disrupt the delicate balance of these ecosystems.”
Conclusion
Understanding food chains and food webs answer key questions about the interconnectedness of life on Earth. By studying these ecological concepts, we gain valuable insights into the complex relationships within ecosystems and the importance of preserving biodiversity. This knowledge empowers us to make informed decisions about conservation and sustainability, ensuring the health of our planet for future generations.
Looking for healthy pet food options? Check out our resources on health extensions dog food near me and free sample of dog food.
FAQ
- What is the difference between a food chain and a food web?
- What is a trophic level?
- What is the role of decomposers in a food web?
- How do human activities impact food webs?
- What is the importance of biodiversity in a food web?
- How does energy flow through a food chain?
- What are some examples of food chains in different ecosystems?
Need further assistance? Contact us! Phone Number: 02437655121, Email: minacones@gmail.com Or visit us at: 3PGH+8R9, ĐT70A, thôn Trung, Bắc Từ Liêm, Hà Nội, Việt Nam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.