America’s food basket circular represents a shift towards a more sustainable and resilient food system. It’s about reducing food waste, supporting local farmers, and creating a closed-loop system where resources are reused and recycled. This approach not only benefits the environment but also strengthens local economies and promotes healthier communities.
Understanding the Concept of America’s Food Basket Circular
The core principle of America’s food basket circular is minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. This involves rethinking how we produce, consume, and dispose of food. Instead of a linear system where food travels from farm to table to landfill, a circular model emphasizes closing the loop. This means finding ways to repurpose food scraps, compost organic matter, and reduce reliance on external inputs.
The Benefits of a Circular Food System
Adopting a circular food system offers numerous advantages. Environmentally, it reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with food waste decomposition and transportation. Economically, it creates new opportunities for local businesses involved in composting, anaerobic digestion, and upcycling food byproducts. Socially, it promotes food security and access to healthy, locally sourced produce.
Imagine a community where food waste is collected and transformed into compost that enriches local farms. These farms, in turn, provide fresh produce to the community, completing the circle. This vision is becoming a reality thanks to initiatives across the country.
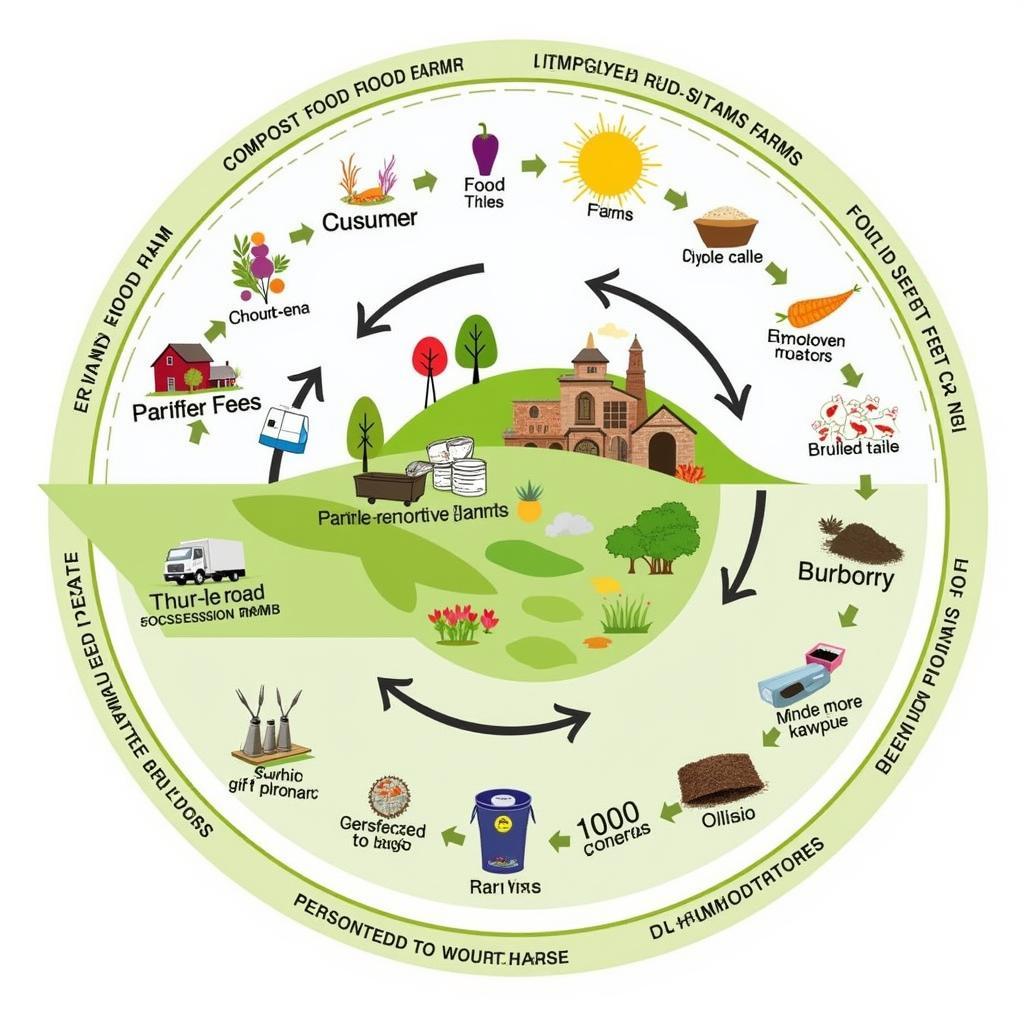 Circular Food System Diagram in America
Circular Food System Diagram in America
Implementing America’s Food Basket Circular: Key Strategies
Several key strategies are crucial for implementing a successful circular food system. These include:
- Source Reduction: Reducing food waste at the source by improving food storage, planning meals, and buying only what’s needed.
- Composting: Diverting food scraps and other organic materials from landfills and transforming them into nutrient-rich compost for gardens and farms.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Using microorganisms to break down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used for energy.
- Upcycling Food Byproducts: Finding creative ways to utilize food byproducts, such as using spent coffee grounds to grow mushrooms or brewing beer from bread crusts.
These strategies, when implemented collectively, can significantly reduce the environmental impact of our food system.
The Role of Consumers in the Circular Economy
Consumers play a vital role in the success of America’s food basket circular. By making conscious choices about what they buy, how they store food, and how they manage food waste, consumers can contribute to a more sustainable future.
For example, planning meals ahead of time can help reduce food waste, while composting food scraps can enrich gardens and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers. Small changes in consumer behavior can have a significant cumulative impact.
 Consumer Choices for a Circular Food System
Consumer Choices for a Circular Food System
Challenges and Opportunities in America’s Food Basket Circular
While the concept of a circular food system offers significant promise, there are also challenges to overcome. These include:
- Infrastructure: Developing the necessary infrastructure for composting, anaerobic digestion, and other resource recovery methods.
- Logistics: Optimizing logistics for collecting and transporting food waste from various sources.
- Consumer Education: Raising awareness among consumers about the importance of reducing food waste and participating in circular economy initiatives.
Despite these challenges, there are also tremendous opportunities for innovation and growth in this emerging sector. New technologies and business models are constantly being developed to address the challenges and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable food system.
“A truly sustainable food system requires a collaborative effort,” states Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in sustainable agriculture. “We need consumers, businesses, and policymakers working together to create a closed-loop system where resources are valued and waste is minimized.”
 Community Composting Initiative in Action
Community Composting Initiative in Action
Conclusion
America’s food basket circular offers a pathway to a more sustainable and resilient food future. By embracing this approach, we can reduce our environmental footprint, strengthen local economies, and create healthier communities. The transition to a circular food system requires collective action, with consumers, businesses, and policymakers playing crucial roles. Let’s work together to build a food system that nourishes both people and the planet. Remember, every small step counts in this journey towards a more sustainable future.
FAQ
- What is a circular food system?
- How can I reduce food waste at home?
- What are the benefits of composting?
- How does anaerobic digestion work?
- What are some examples of upcycling food byproducts?
- How can I support local farmers who practice sustainable agriculture?
- What are the biggest challenges facing the circular food economy?
Need support? Contact us 24/7: Phone: 02437655121, Email: minacones@gmail.com Or visit us at: 3PGH+8R9, ĐT70A, thôn Trung, Bắc Từ Liêm, Hà Nội, Việt Nam.